IoT Edge Runtime with AWS Greengrass. Introduction.
A Beginner's Guide to IoT Edge Runtime using AWS Greengrass
Introduction
In this series, I'll show how to build a solid foundation to deliver your custom business logic on-premise with AWS Greengrass open-source edge runtime.
I'll not deep dive into Lambda at Edge (serverless business logic) or MQTT (message broker) capabilities offered by AWS IoT Core and AWS Greengrass. I'll focus more on plain old java based Rest API server and synchronous calls.
Nevertheless, it great if you can learn the event-driven architecture and rearchitect your solutions with asynchronous communication patterns. Great place to start to learn event -driver architecture is Serverless Land - Event Driven Architecture
Parts
This series consists of four parts, each part is independent of another.
Introduction. In this part, we are talking about the use case and the AWS Greengrass itself
Setup. Here I'll show how to quickly launch Greengrass as a docker image on our computer
Use case
High-level description
I'll focus on the use case calling your custom REST API server deployed at the edge from your local computer, it may be your cloud infrastructure, without using VPN.
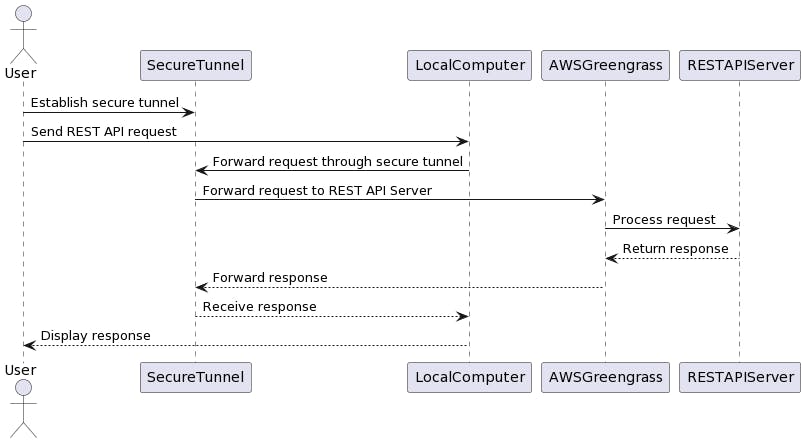
Figure 1. Sequence diagram to call REST API deployed at Edge
In Figure 1 diagram, the User initiates the workflow by sending a REST API request from their local computer. The request is then forwarded through a secure tunnel, established between the LocalComputer and the SecureTunnel component. The SecureTunnel acts as an intermediary, forwarding the request to the REST API Server deployed as a custom component on AWS Greengrass.
The REST API Server, hosted on AWS Greengrass, processes the request and returns a response. The response is then sent back through the secure tunnel, following the reverse path, and received by the LocalComputer. Finally, the LocalComputer displays the response to the User.
Please note that this diagram represents the high-level workflow and may require further details and configuration depending on the specific tools and technologies you are using for the secure tunnel and AWS Greengrass deployment.
Real-world scenario
This use case is the genericization for the deployment and management of smart home automation systems.
In a smart home automation system, various IoT devices such as smart lights, thermostats, door locks, and security cameras are interconnected and controlled through a central management system. This central system allows users to configure and control their smart home devices from a single interface, often through a mobile app or web application.
To enable device configuration, a custom REST API server can be developed and deployed as part of the smart home automation system. This REST API server acts as the bridge between the central management system and the IoT devices deployed throughout the home.
By using a custom REST API server in this smart home automation system, users can conveniently configure and control their IoT devices from a single interface. The REST API server acts as a central hub, allowing for seamless communication between the central management system and the distributed IoT devices, making it easier to manage and personalize the smart home experience.
AWS Greengrass can be used as an edge runtime to run REST API servers and orchestrate IoT devices on-premises.
Overview of AWS Greengrass
AWS Greengrass is a service that extends AWS to edge devices, enabling local processing, messaging, and data caching. It allows IoT devices to act locally on the data they generate while still using the cloud for management, analytics, and storage. Greengrass provides a runtime environment for Lambda functions and connectors, allowing developers to create custom applications and integrations for edge devices.
Figure 2. shows the role of AWS Greengrass, which acts as a gateway between devices and AWS Cloud. As a rule, Gateway is deployed near devices, on-premise.

Figure 2. Greengrass Role as Gateway in IoT Ecosystem
Benefits of using AWS Greengrass
Some benefits of on-premises deployment of Greengrass devices include:
Reduced latency: Local processing of data enables faster decision-making and real-time responses.
Network efficiency: Local processing reduces the amount of data sent to the cloud, saving bandwidth.
Enhanced security: Sensitive data can be processed locally, reducing the risk of exposure during transmission.
Continuous operation: Devices can continue functioning even with intermittent or no internet connectivity.
Cost savings: Reduced data transmission to the cloud can lower associated costs.
But Greengrass is part of the AWS ecosystem which takes the heavy lifting of Gateway core software and tooling to deliver you custom business logic for your use case rather than an easy task :)
Summary
In this part, I described IoT-related use cases for using edge runtime to run the Rest API server for the configuration of smart house components.
I showed that AWS Greengrass offers an open-source edge runtime capable of deploying, running and upgrading our custom applications at the edge.
Let's jump to the next part to configure your first or not :) Greengrass Thing!

